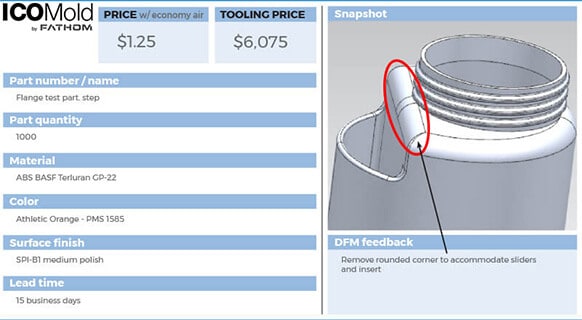
PolyJet 3D Printing
PolyJet (PJ) technology is capable of creating smooth surfaces, thin walls and complex geometries with accuracy as high as 0.1 mm. PJ is the one and only technology that supports a wide selection of materials with properties that range from rubber to rigid and transparent to opaque. It is also possible to 3D print with multiple materials in a single build to achieve combinations of colors and characteristics (e.g. parts made of rigid and flexible materials).
How Does PolyJet 3D Printing Work?
PolyJet is photopolymer-based jetting process that distributes material droplets layer-by-layer onto a build platform (immediately cured by a flash of UV light). At the end of the build process, the object is fully cured and can be handled immediately without post-curing. This technology includes use of a gel-like support material, designed to enable complicated geometries (removed by soaking and/or water jetting).
PolyJet Parts & Images












PolyJet 3D Printers use photopolymers, which are capable of simulating properties ranging from rubber-like to transparent even with high toughness and heat resistance.
Digital materials expand the possibilities by blending two or more base resins to create thousands of material combinations. Customers can achieve full color capabilities, translucencies, Shore A values and other properties for maximum realism in their product designs.
Below is a list of PolyJet materials offered by Fathom. Additional materials available upon request.
| TYPE | MATERIALS | DESCRIPTION |
|---|---|---|
| Simulated ABS | Digital ABS Plus (Ivory) |
|
| Transparent | Vero Clear |
|
| Rigid Opaque | Vero Pure White, Vero Black Plus, Vero White Plus, Vero Yellow, Vero Cyan, Vero Magenta, Vero Blue |
|
| Simulated Polypropylene | Rigur (White) |
|
| Rubber-like | Agilus30 (Clear), TangoBlack+ |
|
| Digital Materials | Predetermined blends of the above materials |
|
*Parts over 250mm in any dimension require quote review.
What Are The Advantages & Disadvantages of PolyJet 3D Printing Technology?
Before you decide to use PolyJet to manufacture your parts, you should be aware of the benefits of this method. These benefits include //
- Complex Geometries With Intricate Details
- Smooth & Detailed Prototypes
- Faster Build Times
- Wide Variety of Material & Color Options
- Good Tensile Strength
PolyJet vs. Stereolithography
SLA and PolyJet sound like similar technologies because they both utilize UV curable materials and lasers, but there are notable differences. The primary difference between the two lies in the build process. SLA uses a vat, laser and a UV oven. PolyJet distributes the material through a printhead and the material is instantly cured by a UV light as soon as it is placed on a platform. Both methods use support material but are removed in different ways. After a part has been produced using stereolithography, the support material must be removed by hand. In PolyJet, the support material is made from a gel-like substance which is easily removed with water blasting or by hand.
Applications of PolyJet
PolyJet has grown to be a popular manufacturing method across a variety of industries. Dental, consumer goods, medical, robotics, aerospace and defense industries all use PolyJet. Applications of PolyJet include //
- Medical // Organ Replicas, Prosthetic Limbs & Joint Replacements
- Dental // Crowns, Bridges & Other Orthodontics
- Consumer Goods // Rapid Prototyping, Injection Modeling & Functional Prototyping
- Flexible Parts That Simulate Traditional Elastomers
- Cosmetic Prototypes That Can Simulate The Look Of Injection Molded Parts
- Parts To Test Fit
- Presentation Models
- Complex Parts
- Master Patterns
- Visual Aids & Models For Presentations
PolyJet Questions Answered (FAQ)
Q: Who Invented PolyJet Technology?
A: In 1998, the Israeli 3D printer manufacturer, Objet Geometries, created PolyJet.
Q: How Much Detail Can Be Achieved Using PolyJet?
A: Fine details can be achieved using PolyJet as it is a high-resolution technology.
Q: Is PolyJet Only For Prototyping?
A: No, end use parts can be created using PolyJet. However, it is important to note that parts made using PolyJet become vulnerable when exposed to UV light for long periods of time.
Q: Can You Eliminate The Support Material From The PolyJet Process?
A: No. Any part with overhangs or spaces has to be filled for support or the part may warped or collapse during the build process.
From design to production, PolyJet offers agility and aesthetics to every stage of the product development cycle. With the widest range of properties available, PolyJet material options allow designers and engineers the ability to create realistic prototypes. Production-level quality allows engineers the ability to more accurately evaluate product look and functionality, streamline production and even open up new possibilities for future products. This technology is also capable of producing molds for urethane casting and injection molding as well as manufacturing aides such as fixtures like a soft jaw for CNC machining.