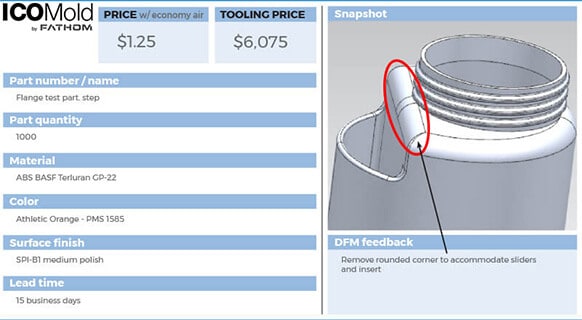
What is CNC Machining Service?
CNC (Computer Numerical Control) Machining is a subtractive manufacturing process that involves using high speed, precision cutting tools to remove material from a blank block. The block is usually made of plastic or metal. The CNC machine carves away material from the block to create the part.
A CNC machine is given a specific set of directions and uses those instructions to cut the part out of a blank. The CNC machine instructions are given in computer code. The code will tell the machine where to place the tooltip, how fast the tooltip should spin, and the coordinates to where the tooltip will move. CNC machines use coordinates on a set axis such as x-, y-, and z-axis. Commonly used CNC machines include vertical milling machines, horizontal milling machines, lathes, routers, and grinders. Parts can be cut out with high precision and easily replicated over and over again. ICOMold by Fathom offers a wide array of plastic machining services by offering not only CNC machines for plastic and metal but plastic injection molding services as well.
Benefits of CNC Machining
CNC Prototyping
A plastic prototype part ensures the product design is sound when starting a new plastic injection-molding project. For most plastic parts, a CNC machined prototype can provide exactly what is needed for testing purposes. CNC machining allows designers to test the form, fit, and function of parts that will be injection molded without the cost to produce the injection mold tooling.
Small Production Run
Plastic injection molding is the ideal process for making hundreds, thousands, or even millions of the same part but it is not cost effective for small runs. CNC plastic machining services are the perfect manufacturing process for making a small quantity of parts. All that is needed is the CAD file and a block of plastic. CNC machining can save customers a substantial amount of money during the prototyping phase or when making only a handful of parts. CNC plastic machining services do not require the time and money needed to produce an expensive mold. Parts can be created directly on the plastic CNC machine. It is the perfect manufacturing process for runs under 100 pieces. Part runs over 200 pieces may be produced cheaper with injection molding.
Quick Turnaround Time
Plastic CNC machining services are fast and efficient. The part can be cut almost immediately after receiving the CAD file. Other manufacturing processes like injection molding will take more time and effort to produce a single part. Plastic injection molding requires a larger upfront cost and many hours of milling to make the mold. CNC plastic machining services do not have any upfront costs and can enter production quickly.
High Quality Parts
CNC plastic machining services have many advantages over manual manufacturing. CNC machining is a more precise process than manual machining and provides exact repeatability. Computer control ensure the machine movement and makes the tools move precisely and simultaneously on their axes to create complex, three-dimensional shapes that would be almost impossible with manual machining.
This accuracy and control makes CNC machining an ideal manufacturing process for jobs that require a high level of precision or repetition. ICOMold by Fathom can hold all tolerances to within +/- 0.2 mm to 0.3 mm. Customers can specify tolerances up to 0.01 in. (0.254 mm) if there are critical areas on the part where tight tolerances are extremely important.
CNC machining can produce more robust parts in plastic then compared to 3D printing. CNC plastic machining services can be done on a wide range of plastic material. In many cases, the same plastic that will eventually be used for injection molding the final part run can be used for CNC machining prototype parts. These parts can then be subjected to the same tests and conditions as the eventual injection molded production parts.
Plastic CNC Machining vs. Plastic 3D Printing
CNC machining is a good choice for making prototypes and low-volume plastic parts. CNC plastic machining services can be done with different materials than those typically used in the 3D printing process. Prototype parts often need to be tested under the same conditions the final injection molded parts will experience. For testing purposes, both the prototype and the final part will need to be made out of the same material. Plastic parts made with 3D printing will be limited to the materials that can be uswed by the 3D printer. Plastic parts made with CNC machining can be made out of a vairty of materials. Plastic parts made with CNC machining will also have better structural integrity than 3D printed parts. Learn more about CNC Plastic Machining.
What is the best plastic to CNC?
The best plastic for CNC machining depends on the intended use for that part. All plastics have different material properties. Some plastics are flexible while other are rigid. Some plastics are more readily able to withstand extreme temperatures and environmental conditions. Some plastics are rated for use in or around the human body while others are not. Speak with the experts at ICOMold by Fathom to find out which plastic is best suited for your project. ICOMold currently offers the following materials for CNC machining:
- ABS
- ABS, Black
- HDPE
- Noryl
- Nylon
- PC
- PEI
- PMMA (Acrylic)
- POM
- PTFE (Teflon)
- PVC
- UHMW
- ULTEM
CNC Metal Machining
ICOMold by Fathom sets a standard tolerance for CNC machined metal at +/- 0.002 in. Customers can request tighter tolerances if required. The hardness of metal will affect the length of time required to machine the part. Using a harder metal like carbon steel requires a slower spindle. The slower spindle speed will take more time to remove the material from the part. A part can be cut nearly four times faster with a softer metal like aluminum when compared to a hard metal like carbon steel. Make sure to consider the type of metal and how long the CNC machining will take when estimating project costs. Learn more about CNC Metal Machining.
Secondary CNC Machining Processes
ICOMold by Fathom offers a wide range of post-processing options. Secondary processes include painting, silk screening, and assembly.
The following is a list of the standard secondary processes offered by ICOMold. Secondary options are available for selection in a dropdown menu in our interactive quotation system. In addition, the experts at ICOMold by Fathom would be happy to discuss your custom process needs.
- Painting
- Inserts
- Silk screening
- Higher tolerance than +/- 0.01 in. (0.254 mm) in plastic
- Custom processes
Types of CNC Machines
There are several types of CNC machines, each with its own functionality to machine different types of parts in different ways.
CNC Mills
CNC mills generally start with a black block of material that removes excess material until only the desired part is left. The CAD file is translated into G-code (or similar code). This code is then uploaded to the CNC mill, where the computer controls the spindle in a three-axis system (X, Y and Z). The code contains the coordinates for the part and the speed at which the spindle should spin. The CNC mill follows the code in order to create parts from plastic or metal.
CNC Lathes
CNC lathes differ from CNC mills as they only move their spindles in a two-axis system (X and Y). CNC lathes take a blank and then spin it at a high RPM. Any cuts made to the blank are uniform on all sides. CNC lathes are used for creating cylindrical pieces that need to have uniform cuts on all sides.
CNC Plasma Cutters
CNC plasma cutters use the same technology as other CNC machines. CNC Plasma cutters are used for cutting parts out of large, flat metal sheets instead of a block of metal. Plasma cutters, like lathes, can only move their tool tip along two axes.
Get an instant quote now!
Go to the ICOMold by Fath plastic injection molding and CNC machining case studies page to see how we helped customers on their projects.